SQL Tutorial for Beginners
SQL is a very easy database Language to learn and it requires no programming background . It was initially known as SEQUEL and is mainly used to query data from database, manipulate the data and retrieve data from relational database. The term Relational database means to relate structured data in the table. SQL is considered as a standard language for relational database management system and it is also known as data-oriented language The power of SQL is with a single command line we can access many records and we can fetch data based on specific criteria.Know More SQL Server Developer Online Course
Table is represented into rows and columns also known as tuple or records and fields. SQL uses ‘;’ as a statement terminator. SQL command fall into Data Definition Language(DDL) , Data Manipulation Language(DML) , Data Query Language(DQL) , Data Control Language(DCL) , Transaction Control Language(TCL) . A database query can be either a select query or a action query .A select query is used to retrieve data using query while an action query asks for additional operations on data like insertion, updating , deletion. Data Definition Language is used to define the structure of the database. Data Manipulation Language is used to manipulate data. Data Query Language is used to extract the data. We can also use various Aggregation Functions in SQL like Count(count the number of the rows in a relation) , SUM(Adds the value of an attribute in a relation) , GROUP BY (Group the records of a relation based on an attribute or group of attribute).
Data Control Language(DCL) is used to assign and revoke database rights and permissions. SQL Supports Distributed Databases as it is capable of running in several computer network at a time. It uses many important clauses like FROM (which indicate the table where the search will be made) , WHERE (Search will be carried out) , ORDER BY ( To sort the results in ascending or descending order).Read More SQL Server Developer Online Training
A Basic SQL query would be like :
SELECT * FROM
TABLE_NAME WHERE CONDITION
ORDER BY COLUMN_NAME;
The most commonly used commands are : Select , Insert , Update , Delete , Create , and Drop which can be used to do many operations in database.
Conditional selections used in the where clause:
| = | Equal |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or equal |
| <= | Less than or equal |
| <> | Not equal to |
SELECT Statement
“SELECT” is a keyword which will select the data which ever you are referring.
Example:
SELECT * from Table1;
Here * denotes all and also we can specify the particular column to SELECT Keyword. Also you can use “DISTINCT” Keyword to fetch unique columns.
WHERE Clause:
“WHERE” Clause is used to filter records.
Example:
SELECT * FROM Table1 where Name=”Rahul”;
The above statement will only display the record containing the Name: Rahul.
Most Commonly used SQL WildCard Characters are : * and ? which means Zero or more characters and single character. If we need to insert multiple values in the WHERE clause then SQL IN Keyword is preferred.
UPDATE Statement:
“UPDATE” Statement is used to modify the existing record in the table.
Example:
UPDATE Table1 Set Location=”Chennai” where Name=”Rahul”;
Here Set is used to change the existing data with the new one based on the condition.
DELETE Statement:
“DELETE” statement is used to delete the existing records in the table.
Example:
DELETE From Table1 where Name=”Rahul”;
INSERT INTO Statement:
“INSERT INTO” is used to insert new records in the table.
Example:
INSERT INTO Table1 (Name,Location) values(“Ravi”,”Chennai”);
We have a way to impose rule to the data in the table which is commonly known as SQL Constraints and the commonly used are
- NOT NULL (To ensure column doesn’t contain null values)
- UNIQUE (To ensure unique values in a column)
- Primary Key (Not Null and Uniquely identifies each row in a table)
- Foreign key(Referring primary key in another table)
Note: A Field with a null value is considered as no value and also NULL Value is different from a Zero or a field that contains spaces.
We have a concept in SQL called Key which means single or combination of multiple fields in a table).
There is a concept called SQL VIEW which refers to a virtual table which contains rows and columns.
We also have SQL Union Operator which is used to combine result set of two or more SELECT statements. There is a difference between Union and Union ALL as Union returns all the values whereas Union ALL returns only the distinct values.
SQL Aliases are used to give a table temporary name and it is used when we are using more than one tables.
We also have a concept called SQL TOP which is used to select how many records to be displayed in the output. Also LIMIT is used to return the limited number of results.
Hope I have covered few topics in SQL which are commonly used to give a glimpse of the course.Know More SQL Server Developer Training
SQl Joins
We have a concept of SQL JOIN which is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on common column between the tables.
There are five types of SQL Joins :
- SQL Inner Join (returns matching values)
- SQL Left Join (returns all records from the left table and matching records from the right table)
- SQL Right Join (returns all records from the right table and matching records from the left table)
- SQL Full Join (returns matched records from left and right table)
- SQL Self Join (returns data based on the condition and same table is joined with itself)
Inner Join:
Used to retrieve all records from table A and table B where the join condition is met – retrieves common records from both the tables based on the join condition.
Example:
select columns from tableA t1
inner join tableB t2
on t1.col=t2.col;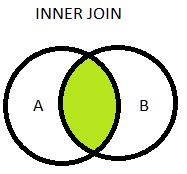 Left Join (Left Outer Join):
Left Join (Left Outer Join):
Used to retrieve all records from table A along with records from table B for which the join condition is met – retrieves all table A records, unique columns of table B and appends NULL values to table B columns if values are empty.
Example:
select columns from tableA t1
left join tableB t2
on t1.col=t2.col;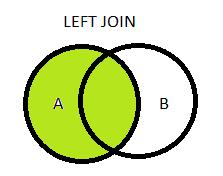
Right Join (Right Outer Join):
Used to retrieve all records from table B and subsequent records of table A where the join conditions are met.
Example:
select columns from tableA t1
right join tableB t2
on t1.col=t2.col;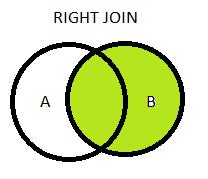
Full Join (Full Outer Join):
Used to retrieve all records from both the tables including irrespective of the join condition – retrieves all the records even if the join condition is not met
Example:
select columns from tableA t1
full join tableB t2
on t1.col=t2.col;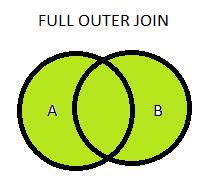
SQL- Select Statements
This statement is the most frequently used statement in SQL. This used to fetch the data from the database which we store in a table. We can fetch the complete record of the table either we can apply some condition with a select statement that will be giving result set or record based on the condition.
We can specify the column as well which has to fetch from the table or can fetch all the columns of the table, It completely depends on how you are going to write the syntax for the select statement. If you have applied some rules or conditions on the select statement first it is going to filter the data based on the same and include all the data to be fetched for the respective columns.
The database driver evaluates the select statement as first and last clauses to build the result-set and the same will be shown as the final result.
Syntax – Below is the syntax for the select statement.
If you want to select all the columns from the table.
SELECT * FROM TABLE_NAME;
If you want to select some specified columns from table.
SELECT COL1,COL2,COL3,COL5 FROM TABLE_NAME;
Now let see how this statement works into real-time and how we used to apply rules/condition on the select statement.
SELECT [DISTINCT] , columns [column [AS aliasname]} FROM tableName [alias] [WHERE condition][GROUP BY fieldName(s)][HAVING condition] ORDER BY columnname;
SELECT – This keyword database know that you want to fetch the data.
DISTINCT
This used to get a unique record for the column.
[column AS aliasname] – This can be given for column and table as well. Mostly this is used to remove ambiguity error or to make a short select statement. This can be applied to fetch the different columns from different tables.
WHERE – This is optional and used to apply to put a condition on a column which filters the data while fetching the records.
GROUP BY – This is used to show the result-set as a group for the same values in the columns.
HAVING – This is also used to apply criteria and work with GROUP BY
ORDER BY – This is used to apply sorting order on records/result-set
Expressions in SELECT Statement? – Many arithmetic operators can be used with a select statement like division, multiplication, addition, subtraction. If more than one operator is used then it works based on the precedence which used to be done left to right and different based on parentheses along with used multiple operators.
Below is the EMPLOYEE_DETAILS having the following records.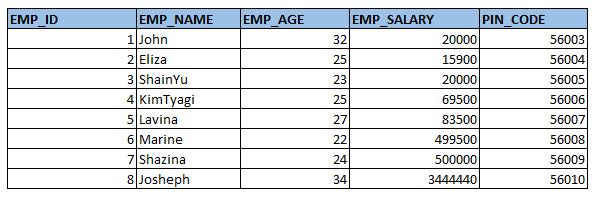
EMPLOYEE_DETAILS
Let’s fetch a few columns – EMP_ID , EMP_NAME,EMP_AGE from the above table.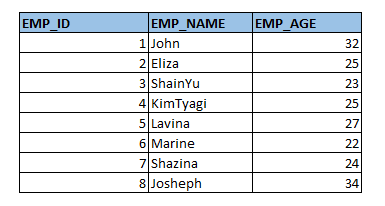
SELECT EMP_ID,EMP_NAME,EMP_AGE FROM EMPLOYEE_DETAILS;
Let’s write the query now to select all the columns, following is the same.
SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE_DETAILS;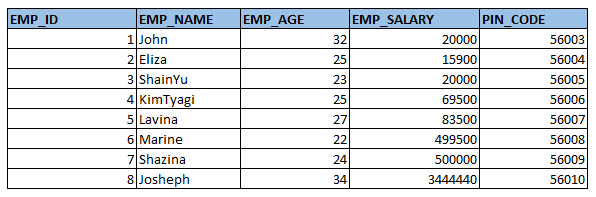
NESTED SUBQUERY
- NESTED queries it is nothing but a query which can return the data to the main query giving more detriments of the retrieving data and we are Where Clause using in embedded queries.
- It can be using in the languages DDL,DML for giving the commands Insert, Delete, Update, Select, Truncate using of the Logical operators <,>,<>,= using in the command / Statements in the given data.
SYNTAX:
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name [operator] (SELECT column_name
FROM table_name1, [table_name2]..
WHERE condition)
WHERE:
- We are creating the Database, table and fields for giving appropriate data for all the fields.
- Consider a table as a student and we are providing the data for oldest database for the student details in the college database and using the query for displaying all the details of the students.



Comments
Post a Comment